New to Voyager? Please start here.
Monitor HAProxy using Prometheus
This tutorial will show you how to monitor Voyager managed HAProxy pods using builtin Prometheus scraper.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using Minikube.
Now, deploy Voyager operator following instructions here.
To keep things isolated, this tutorial uses a separate namespace called demo throughout this tutorial. Run the following command to prepare your cluster for this tutorial:
$ kubectl create namespace demo
namespace "demo" created
$ kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 45m
demo Active 10s
kube-public Active 45m
kube-system Active 45m
Note that the yaml files that are used in this tutorial, stored in docs/examples folder in GitHub repository voyagermesh/docs.
Create Ingress
We are going to use a nginx server as the backend. To deploy nginx server, run the following commands:
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx -n demo
kubectl expose deployment nginx --name=web --port=80 --target-port=80 -n demo
Now create Ingress ing.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/appscode/voyager/v2021.04.24-rc.0/docs/examples/monitoring/builtin-prometheus/ing.yaml
ingress "stats-ing" created
apiVersion: voyager.appscode.com/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: stats-ing
namespace: demo
annotations:
ingress.appscode.com/type: 'NodePort'
ingress.appscode.com/stats: 'true'
ingress.appscode.com/monitoring-agent: 'prometheus.io/builtin'
spec:
rules:
- host: voyager.appscode.test
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: web
servicePort: 80
Voyager operator watches for Ingress objects using Kubernetes api. When a Ingress object is created, Voyager operator will create a new HAProxy deployment and a NodePort Service with name voyager-{ingress-name}. Since ingress.appscode.com/stats annotation was configured, a stats service object is configured accordingly. Here,
| Keys | Value | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ingress.appscode.com/stats | bool | "false" |
Required. If set, HAProxy stats will be exposed |
| ingress.appscode.com/monitoring-agent | string | Required. Indicates the monitoring agent used. Here built-in scraper in Prometheus is used to monitor the HAProxy pods. Voyager operator will configure the stats service in a way that the Prometheus server will automatically find out the service endpoint and scrape metrics from exporter. |
You can verify it running the following commands:
$ kubectl get pods,svc -n demo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
po/nginx-8586cf59-r2m59 1/1 Running 0 1m
po/voyager-stats-ing-5bf6b54949-5zs4x 2/2 Running 0 1m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
svc/voyager-stats-ing NodePort 10.111.51.103 <none> 80:31094/TCP 1m
svc/voyager-stats-ing-stats ClusterIP 10.97.119.249 <none> 56789/TCP,56790/TCP 1m
svc/web ClusterIP 10.98.249.140 <none> 80/TCP 1m
$ kubectl get svc -n demo voyager-stats-ing-stats -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
ingress.appscode.com/origin-api-schema: voyager.appscode.com/v1beta1
ingress.appscode.com/origin-name: stats-ing
monitoring.appscode.com/agent: prometheus.io/builtin
prometheus.io/path: /voyager.appscode.com/v1beta1/namespaces/demo/ingresses/stats-ing/metrics
prometheus.io/port: "56790"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
creationTimestamp: 2018-02-25T21:48:24Z
labels:
feature: stats
origin: voyager
origin-api-group: voyager.appscode.com
origin-name: stats-ing
name: voyager-stats-ing-stats
namespace: demo
resourceVersion: "317"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/demo/services/voyager-stats-ing-stats
uid: 9ac02c7c-1a75-11e8-a133-080027640ad5
spec:
clusterIP: 10.97.119.249
ports:
- name: stats
port: 56789
protocol: TCP
targetPort: stats
- name: http
port: 56790
protocol: TCP
targetPort: http
selector:
origin: voyager
origin-api-group: voyager.appscode.com
origin-name: stats-ing
sessionAffinity: None
type: ClusterIP
status:
loadBalancer: {}
We can see that the service contains these specific annotations. The Prometheus server will discover the exporter using these specifications.
prometheus.io/path: ...
prometheus.io/port: ...
prometheus.io/scrape: ...
Deploy and configure Prometheus Server
The Prometheus server is needed to configure so that it can discover endpoints of services. If a Prometheus server is already running in cluster and if it is configured in a way that it can discover service endpoints, no extra configuration will be needed. If there is no existing Prometheus server running, rest of this tutorial will create a Prometheus server with appropriate configuration.
The configuration file to Prometheus-Server will be provided by ConfigMap. The below config map will be created:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: prometheus-server-conf
labels:
name: prometheus-server-conf
namespace: demo
data:
prometheus.yml: |-
global:
scrape_interval: 5s
evaluation_interval: 5s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'kubernetes-service-endpoints'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme]
action: replace
target_label: __scheme__
regex: (https?)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port]
action: replace
target_label: __address__
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_name
$ kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/appscode/voyager/v2021.04.24-rc.0/docs/examples/monitoring/builtin-prometheus/demo-1.yaml
configmap "prometheus-server-conf" created
Now, the below yaml is used to deploy Prometheus in kubernetes :
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: prometheus-server
namespace: demo
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: prometheus-server
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: prometheus-server
spec:
containers:
- name: prometheus
image: prom/prometheus:v2.1.0
args:
- "--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml"
- "--storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus/"
ports:
- containerPort: 9090
volumeMounts:
- name: prometheus-config-volume
mountPath: /etc/prometheus/
- name: prometheus-storage-volume
mountPath: /prometheus/
volumes:
- name: prometheus-config-volume
configMap:
defaultMode: 420
name: prometheus-server-conf
- name: prometheus-storage-volume
emptyDir: {}
Now, run the following command to deploy prometheus in kubernetes:
$ kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/appscode/voyager/v2021.04.24-rc.0/docs/examples/monitoring/builtin-prometheus/demo-2.yaml
clusterrole "prometheus-server" created
serviceaccount "prometheus-server" created
clusterrolebinding "prometheus-server" created
deployment "prometheus-server" created
service "prometheus-service" created
Prometheus Dashboard
Now to open prometheus dashboard on Browser:
$ kubectl get svc -n demo
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
voyager ClusterIP None <none> <none> 59m
mgo-mon-prometheus ClusterIP 10.104.88.103 <none> 27017/TCP,56790/TCP 59m
prometheus-service LoadBalancer 10.103.201.246 <pending> 9090:30901/TCP 8s
$ minikube ip
192.168.99.100
$ minikube service prometheus-service -n demo --url
http://192.168.99.100:30901
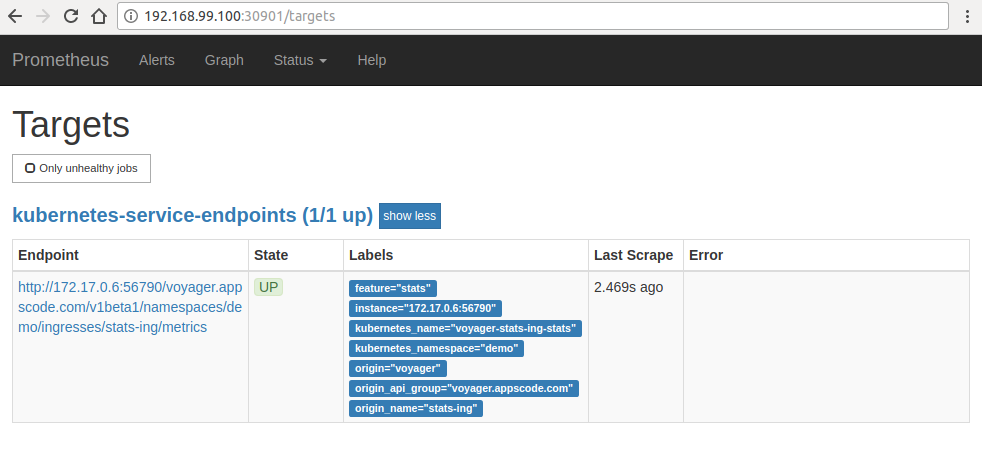
Now, open your browser and go to the following URL: http://{minikube-ip}:{prometheus-svc-nodeport} to visit Prometheus Dashboard. According to the above example, this URL will be http://192.168.99.100:30901.
Now, if you go the Prometheus Dashboard, you should see that the HAProxy pod as one of the targets.
Cleaning up
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
$ kubectl delete ns demo
namespace "demo" deleted